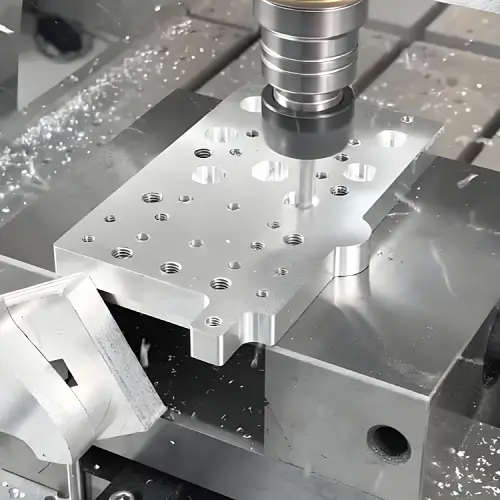
CNC Machining vs Conventional Machining: What’s the Difference?
CNC machining and conventional machining are two common ways to produce metal and plastic parts, but they differ fundamentally in how cutting is controlled. In CNC machining, tool movement follows predefined digital instructions, while conventional machining relies on continuous manual control. This difference affects accuracy, consistency, setup effort, and how easily parts can be produced …