Friction stir welding
Solid-state welding · High strength · Green and environmentally friendly
Introduction to Friction Stir Welding Technology
Friction Stir Welding (FSW) is an advanced solid-state joining technique invented in the UK and further developed in China. It uses a high-speed rotating tool to generate frictional heat at the joint, softening the material to a plastic state without melting. The mechanical stirring action mixes the softened materials, creating a strong metallurgical bond. This process avoids defects like porosity and hot cracking common in fusion welding, making it ideal for high-quality joining of lightweight materials such as aluminum and magnesium alloys.
Welding technology advantages
Friction stir welding offers advantages such as low heat input, minimal deformation, and absence of fusion welding defects. It enables high-strength joining without melting the material, especially for lightweight materials like aluminum and magnesium alloys. It effectively reduces energy consumption and welding residual stress, while improving joint performance and process reliability.
Some applicable materials
| Material Category | Suitability | Typical Examples | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lightweight Non-Ferrous Metals | Highly Suitable | Aluminum Alloys (e.g., 5xxx, 6xxx, 7xxx series), Magnesium Alloys, Copper Alloys | Excellent weldability, free from fusion welding defects |
| Dissimilar Metal Combinations | Conditionally Suitable (process optimization required) | Aluminum-Copper, Aluminum-Steel, Magnesium-Aluminum | Interface bonding control is critical |
| Titanium Alloys | Limited Suitability (due to high melting point) | Pure Titanium, Selected Titanium Alloys | Requires wear-resistant tools and high processing parameters |
| Steel | Partially Suitable (better with low-carbon steels) | Low-Carbon Steel, Stainless Steel | High melting point leads to significant tool wear |
| Thermoplastics | Experimental Applications | PE, PP, PVC | Low-temperature FSW processes still under development |
| Brittle Materials | Not Suitable | Cast Iron, High-Carbon Steel | Prone to cracking or deformation |
Application Areas
Aerospace: Welding of aluminum alloy components such as aircraft fuselage and wings
Rail Transit: Manufacturing of high-speed rail and metro aluminum alloy car bodies
Automotive Industry: Battery trays for new energy vehicles and lightweight car bodies
Shipbuilding: Welding of large aluminum alloy decks and bulkheads
Electronics and Electrical Appliances: Precision heat sink and housing connections
Energy Sector: Nuclear power pipelines and renewable energy equipment
Dissimilar Materials: Specialized joints for aluminum-steel combinations
Some of our welding equipment

FSW-BL3020
Maximum welding depth! 10mm/upgradeable to 20mm Welding stroke XYZ: 3000x2000x500mm

FSW-BL2520
Maximum welding depth: 10mm/upgradeable to 20mm Welding stroke XYZ: 2500x2000x500mm

FSW-A10mini
Maximum welding depth: 0mm/upgradeable to 20mm Welding travel XYZ: 500x600x400mm

FSW-A10
Maximum welding depth: 10mm/upgradeable to 20mm Welding travel XYZ: 600x1200x400mm
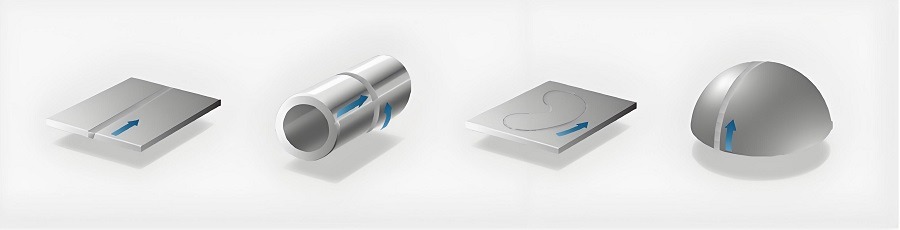
Friction stir welding joint geometry

Butt welding

Lap welding

Pipes and plates

T-welds

Fillet welds

Double fillet welds
Other welding methods
jeek
We support small batch customization, sample trial production and structural optimization suggestions to adapt to the size, material and application scenario requirements of different projects, and can respond quickly and flexibly adjust welding solutions.
Get started quickly
Production of your parts
We ensure that all information provided and uploaded content is kept strictly confidential and secure.
